Light and sound are both waves, what is the difference between them?
Waves are a common phenomenon of propagation in nature, and we often encounter various forms of waves in our daily lives. Although light and sound are the two most familiar fluctuation phenomena and both belong to the category of waves, their nature and propagation are fundamentally different. So, what are the differences between light and sound waves?

The occurrence of thunder involves both light and sound waves
What’s a wave?
First of all, we need to understand what a “wave” is. In physics, a wave is the phenomenon of energy propagation through a medium, usually manifested as the transmission of vibrations. Waves can be divided into two categories: mechanical waves and electromagnetic waves. Mechanical waves depend on a medium (e.g., air, water, or a solid) for their propagation, while electromagnetic waves do not depend on a medium and can propagate in a vacuum.
Whether it is light or sound waves, they are fluctuating phenomena with certain basic properties such as wavelength, frequency, and amplitude. Although they propagate in different ways, their fundamental characteristic lies in the transfer of energy.
Light waves: representative of electromagnetic waves
Light is an electromagnetic wave, which belongs to a special type of wave. Electromagnetic waves consist of fluctuations of electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to each other and change periodically, and light waves are the manifestation of such volatility. According to the theory of electromagnetic waves, the propagation of light does not depend on any material medium; it can propagate in a vacuum, so that light can propagate freely in the empty universe.
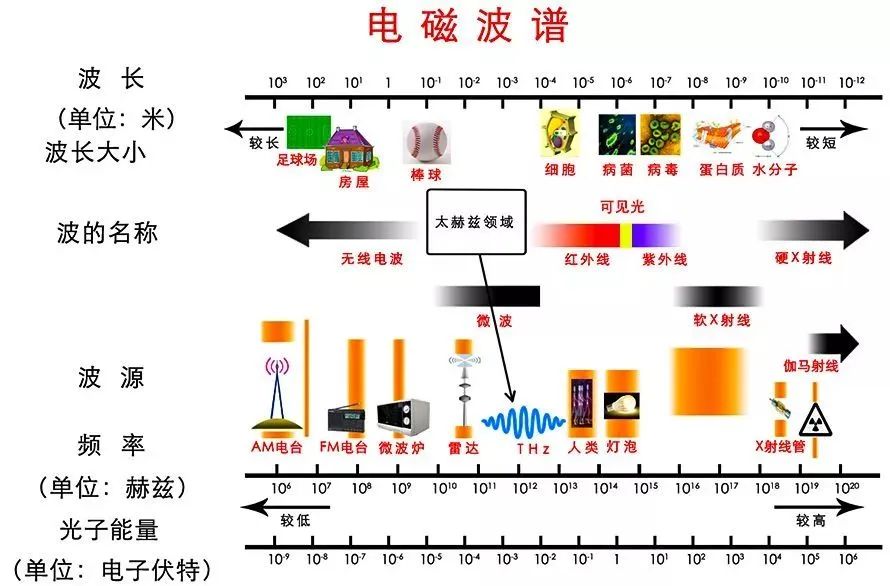
electromagnetic spectrum
Light waves travel so fast that the speed of light in a vacuum is about 299,792,458 m/s (about 300,000 km/s), which means that light can travel around the Earth seven and a half times in one second. The wavelength and frequency of light waves determine the color and properties of light. For example, red light has a longer wavelength, while violet light has a shorter wavelength. Additionally, red light waves have a lower frequency, whereas violet light waves have a higher frequency.
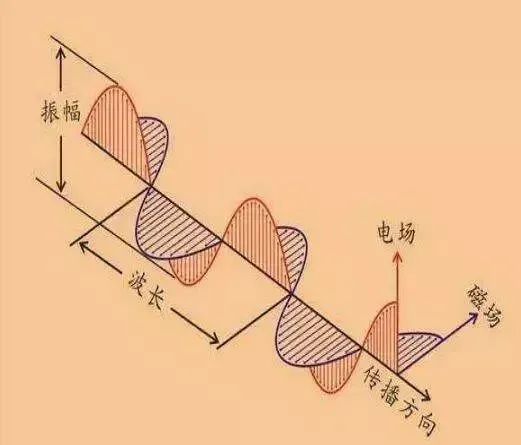
Electromagnetic waves consist of fluctuations of electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to each other and change periodically
Since light waves propagate by the mutual change of electric and magnetic fields, it does not require any medium; light is able to propagate in a vacuum and can travel through transparent media such as air, glass, water, and so on. Light waves are not just a visual representation of what we see, but also include other types of electromagnetic waves that we cannot see, such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared rays, and ultraviolet rays.
Sound waves: a manifestation of mechanical waves
Unlike light waves, sound waves are a type of mechanical wave. Mechanical waves are fluctuations that need to rely on a material medium to propagate and cannot exist in a vacuum. The propagation of sound waves is formed by air molecules (or molecules in other media) vibrating against each other. The propagation of sound waves transfers energy through collisions and vibrations between molecules.
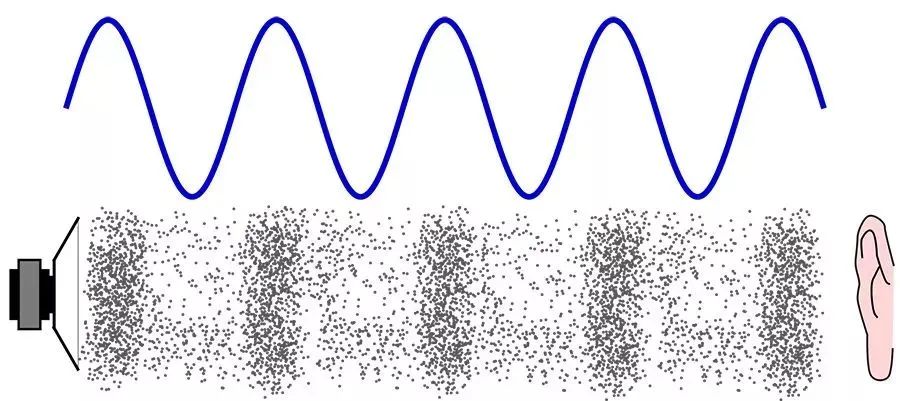
Sound waves travel by transferring energy through collisions and vibrations between molecules
Sound usually travels slowly, about 343 m/s in air (at 20°C), a million times slower than the speed of light. The speed of sound propagation is not only related to the nature of the medium, but also to the temperature and density of the medium. For example, in water, sound waves travel at a speed of about 1500 m/s; in solids such as steel, the speed of sound waves is even faster.

Propagation of sound waves
Sound waves require a medium (e.g., air, water, or a solid) to travel; they cannot travel in a vacuum. The wavelength and frequency of sound waves determine the characteristics of sound. For example, low-frequency sounds (e.g., bass) have longer wavelengths and lower frequencies, while high-frequency sounds (e.g., sharp treble) have shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies. It is the frequency that is closely related to the height of the sound we hear.
The main difference between light and sound
While there are many similarities between light and sound waves in the nature of their fluctuations, there are some significant differences in the way they propagate and in their nature. The following are their main differences:
- Different modes of propagation:
Light waves are electromagnetic waves that can propagate in a vacuum, but also in transparent substances, such as air, water, glass, etc.. Sound waves are mechanical waves, must rely on the material medium (such as air, water, solid) to propagate, can not propagate in a vacuum.
- Propagation speed is different:
The propagation speed of light waves is extremely fast, about 3 × 10^8m/s in a vacuum, much faster than sound waves. The propagation speed of sound waves is relatively slow, depending on the medium. In the air is about 343
m/s, in water and solid propagation is faster.
- The nature of the wave is different:
Light waves are transverse waves; the direction of vibration of the electric and magnetic fields is perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation. And sound waves are longitudinal waves, the vibration direction of the particles of the medium is the same as the direction of wave propagation.
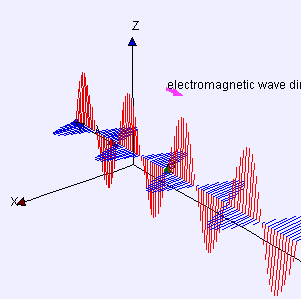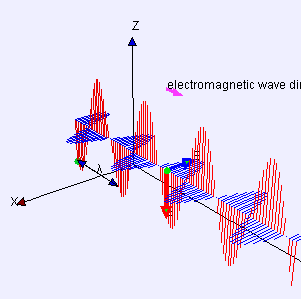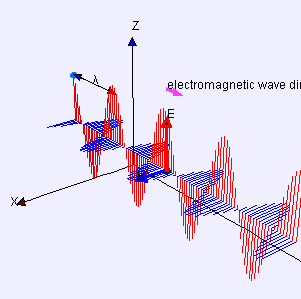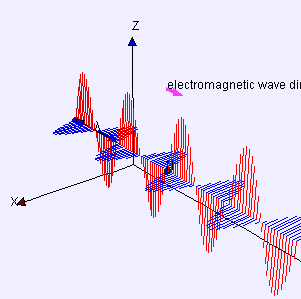
Electromagnetic wave animation
- Dependence on the medium is different:
Light waves do not depend on any material medium and can be propagated in a vacuum, which is why the sun’s light can traverse the vast universe. And sound waves must rely on the medium of propagation; they can not be propagated in a vacuum. Therefore, astronauts in space are unable to hear any sound.
- Perceptibility is different:
Light waves are fluctuations that we perceive through vision, and the color, brightness, direction, and other properties of light are perceptible to our eyes. And sound waves are fluctuations that we perceive through hearing; the height, loudness, timbre, etc. of sound are recognized through the ears.
Differences between light and sound in practical applications
The applications of light and sound in many fields also demonstrate their respective uniqueness. For example, in the field of communications, fiber-optic communications utilize the high speed and low attenuation characteristics of light waves to achieve high-speed long-distance communications, while sound is mainly used in communications such as telephony and broadcasting. In the field of medicine, ultrasound (a type of sound wave) is widely used for ultrasonic examinations and treatments, while lasers (a type of light wave) play an important role in surgery and optical treatments.
echography
In addition, the propagation properties of light and sound in the natural environment affect every aspect of our daily lives. For example, we can determine the distance by the difference in the speed of light (e.g., the time difference between lightning and thunder), while the reflection and propagation speed of sound waves help us in sonar detection and localization.
To summarize, although light and sound waves are both fluctuating phenomena, they are fundamentally different in terms of propagation mode, speed, and medium dependence. Light waves are electromagnetic waves, do not depend on the medium, the propagation speed is extremely fast, while sound waves are mechanical waves, and must depend on the medium of propagation, the speed is relatively slow. These differences make their role and application in nature and human society have their own uniqueness.

